How Does the Aging Baby Boom Generation Affect the Population Pyramid?

The demographic transition model
The demographic transition model shows population change over time. Information technology studies how birth rate and expiry charge per unit affect the total population of a country.
The five stages of the demographic transition model:
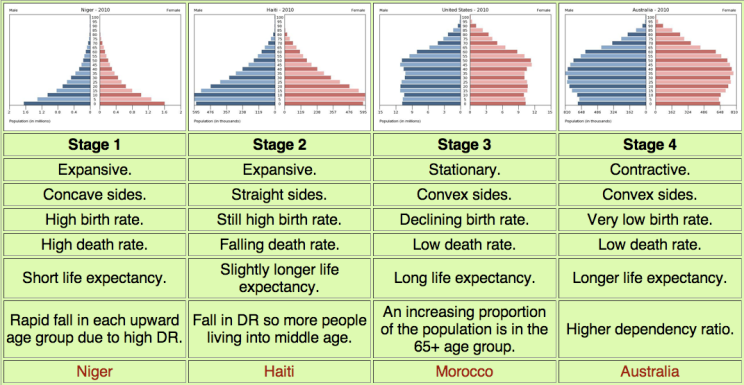
- Total population is low but information technology is balanced due to high birth rates and high death rates.
- Total population rises every bit death rates fall due to improvements in wellness care and sanitation. Birth rates remain high.
- Total population is notwithstanding rising speedily. The gap between nativity and death rates narrows due to the availability of contraception and fewer children being needed to work – due to the mechanisation of farming. The natural increase is loftier.
- Total population is high, simply it is balanced by a depression birth charge per unit and a low death rate. Birth control is widely available and there is a desire for smaller families.
- Total population is high but going into decline due to an ageing population. There is a continued desire for smaller families, with people opting to have children later in life.

Every bit a country passes through the demographic transition model, the full population rises. Most LEDCs are at phase 2 or 3 (with a growing population and a high natural increase). Most MEDCs are now at stage 4 of the model and some such as Federal republic of germany have entered stage 5.
The demographic transition model
Equally populations move through the stages of the model, the gap between birth rate and death rate first widens, then narrows. In stage 1 the two rates are balanced. In stage two they diverge, every bit the decease rate falls relative to the birth rate. In stage 3 they converge again, as the nativity rate falls relative to the expiry rate. Finally, in stage iv the death and birth rates are balanced again just at a much lower level.
Limitations of the model
- The model was adult subsequently studying the experiences of countries in Western Europe and Due north America. Atmospheric condition might be different for LEDCs in dissimilar parts of the world.
- The original model doesn't take into account the fact that some countries at present take a declining population and a 5th stage. Most texts will now show this phase equally it is relevant to an increasing number of MEDCs in the 21st century.
Population structure and population pyramids
Population structure means the 'make upward' or composition of a population. Looking at the population construction of a identify shows how the population is divided up between males and females of different age groups.
Population structure is unremarkably shown using a population pyramid. A population pyramid can exist drawn up for any surface area, from a whole continent or country to an individual town, city or village.
The post-obit graphs testify the population pyramids of an MEDC (the Britain) and an LEDC (Mozambique), for 2000.
Population pyramid for the UK 2000/2016


- Detect how in the U.k. 2000 pyramid at that place is a bulge in the area of the 30-34 and 35-39 age groups, with the numbers thereafter reducing fairly steadily as the ages increase. This matches phase iv of the demographic transition model.
- A narrow base that shows a low birth, so not very young
- A broad shape at the top that shows a high proportion of people living longer. Women live longer than men.
- The burl in the middle of the pyramid showing a baby boom /high charge per unit of births) related to a proper period, no wars, growth, etc., over 1960´s and 1970´s.
- And compare to 2016 pyramid at that place is a bulge in the area 45 -54 (16 years later than the burl in 2000 Britain´s pyramid). Births have decreased lightly, and life expectancy have increased. In that location are more ageing people.
Population pyramid for Mozambique 2000/2016


- In this graph, discover that in 2000 the 0-4 age group contained the largest number of people, with the numbers thereafter declining steadily as the ages increase. The graph matches phase ane in the model.
- A narrow shape on the meridian shows a depression proportion of people living in old-age and a high death charge per unit. Women live longer than men. Depression life expectancy.
- The middle shapes prove many young dependants. In 15-19 aged-grouping there is an indent high mortal rate than normal related to state of war, famine, disease, emigration, etc.
- A wider shape on the base shows a loftier birth rate and a big number of children. Fewer baby girls than baby boys, just boys had a high infant mortal rate than girls.
- 2016 pyramid show us very similar data. Not many differences in Births, nor in deaths.
Analysing population pyramids
Key things to know about population pyramids
- The shape of a population pyramid can tell united states of america a lot about an area'southward population.
- It gives the states information about birth and death rates as well as life expectancy.
- A population pyramid tells us how many dependants at that place are. At that place are ii groups of dependants; immature dependants (aged below xv) and elderly dependants (aged over 65).
- Dependants rely upon the economically active for economic support.
- Many LEDCs have a high number of young dependants, whilst many MEDCs have a growing number of elderly dependants.
How do pyramids change over time?
- A population pyramid that is very triangular (eg Mozambique in 2000) shows a population with a loftier number of young dependants and a low life expectancy.
- A population pyramid that has fairly direct sides (more like a barrel) shows a population with a falling birth rate and a ascension life expectancy.
- Over fourth dimension, as a country develops, the shape changes from triangular to barrel-like.
- Places with an ageing population and a very depression nascence rate would have a structure that looks like an upside-down pyramid.
Population numbers alter over time, influenced by births, deaths and migration into or out of the expanse. Global population levels, having grown slowly for most of man history, are now rising.
Typical pyramids

| MEDC/LEDC Occupational Structures | |||||
| Main | Secondary | Tertiary | |||
| MEDC | Very low. Machines have largely replaced human labour on the farms. | Depression. Automation is increasingly replacing human labour in factories. Globalisation is leading to a shift of manufacturing jobs to the NICs. | High. Large numbers are employed in education, health, administration and the cognition economy | ||
| LEDC | Large primary sector (farming). Exports are commonly primary commodities. | Low. Tariff barriers imposed by the trading blocs such as the EU forbid the export of cheap manufactured products. The domestic market place is very small. | Large service sector. Many employed in the breezy economic system. | ||
| NIC | Shrinking primary (farming) sector. | Secondary sector is large and growing (transnationals). | Minor but growing tertiary sector to serve the needs of the transnationals | ||
http://world wide web.bbc.co.united kingdom of great britain and northern ireland/schools/gcsebitesize/geography/population/population_change_structure_rev1.shtml
http://geographyfieldwork.com/PopulationStructure.htm
Source: https://2puertadecuartos.wordpress.com/2017/05/05/how-to-comment-a-population-pyramid/
0 Response to "How Does the Aging Baby Boom Generation Affect the Population Pyramid?"
Post a Comment